
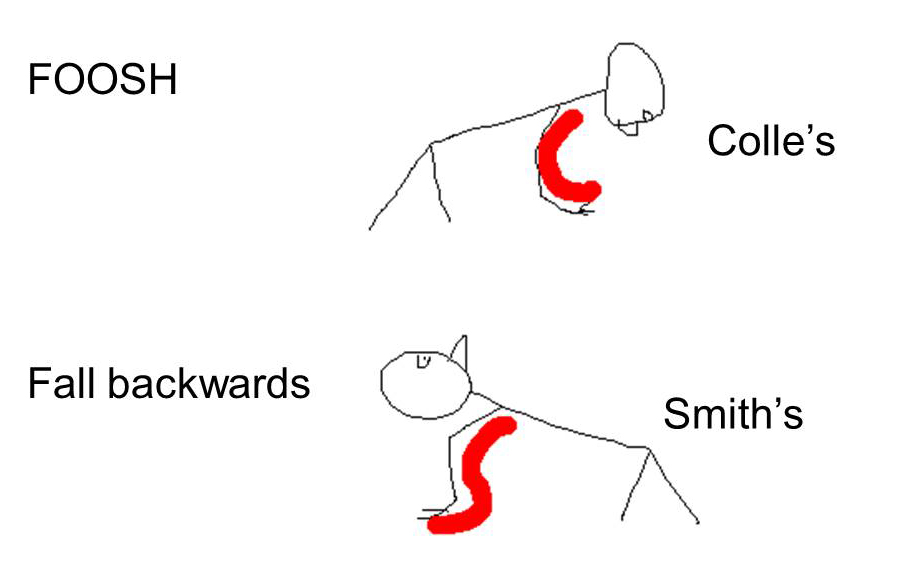
Smith fractures are the opposite: The broken end of your bone points forward. (Colles fracture) or hyperflexion (Smiths fracture), and radial or cubital deviation which result in different types of fracture traces and displacements. It is argued that these injuries, therefore, need open stabilization 1. If you’re diagnosed with a Colles fracture, the broken piece of your wrist bone (radius) points backward. In patients with distal radius fractures, a concomitant ulnar styloid fracture does not affect outcomes 3, and a lack of union of these fractures does not significantly affect late functional results 1,2. Fractures at the very base of the ulnar styloid can cause instability of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) and disruption of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) insertion at the ulnar fovea. In children, up to 15% of ulnar styloid process fractures may be occult as the ulnar styloid process does not start to ossify until 5-9 years 2. Your doctor will categorize your fracture according to how and where the bone broke. Hence in fractures of the distal radius, the former results in the common dorsal angulation of the Colles fracture, whereas the latter in the rarer volar.

Sometimes the fractures may not seem very apparent on x-ray if there is no displacement. The fracture is easy to recognize on plain film. In the pediatric and adolescent forearm, it should be remembered that in very rare situations the ulnar styloid can arise from a separate ossification center, but mostly separation of the ulnar styloid is caused by injury 1. Most common are small avulsion fractures involving the tip of the ulnar styloid with transverse fractures through the base less common 2. For a discussion of this fracture refer to the article on Smith fractures. In fact, the reverse Barton fracture is a type II Smith fracture: oblique distal intra-articular radial fracture 1,2. Wrist fracture in which the distal end of the radius is displaced forwards.
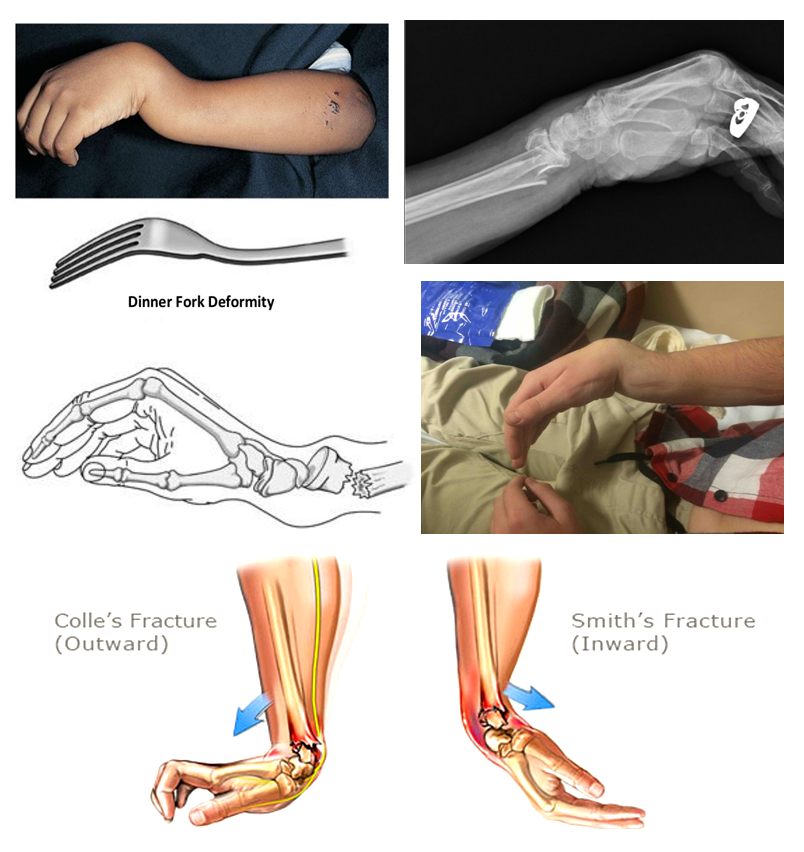
Usually, this kind of fracture occurs as the result of a fall on an outstretched arm and is often associated with a distal radius fracture 1. 51 Evidence 169 Video/Pods 30 Techniques 4 4.5 ( 177 ) 56 Topic Podcast Images Summary Distal radius fractures are the most common orthopaedic injury and generally result from fall on an outstretched hand. Reverse Barton fractures, also known as volar type Barton fractures, represent an intra-articular distal radial fracture with volar displacement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
